New publication from Anders Nykjær's group published in the Journal of Clinical Investigations
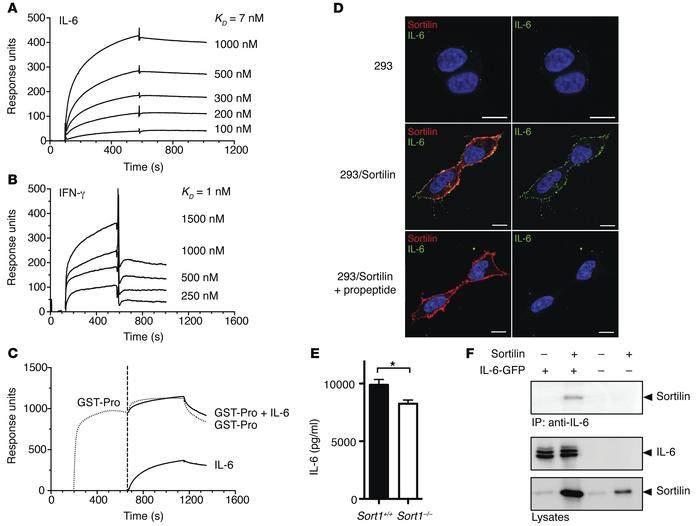
In this study "Targeting sortilin in immune cells reduces proinflammatory cytokines and atherosclerosis", the researchers identify a new mechanism critically involved in the development of ischemic heart disease. They report that sortilin, a multifunctional receptor enriched in neurons, has a surprising role outside the nervous system by facilitating the release of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and IFN-gamma from immune cells in the vessel wall. In a mouse model of atherosclerosis, deletion of sortilin expression substantially reduced the development of both early and late atherosclerotic lesions independent on plasma cholesterol. The data suggest that pharmacological inhibition of sortilin in immune cells may attenuate inflammation and reduce atherosclerosis.